laboratory analysis of pleural fluid|pleural fluid lab tests : wholesale INTRODUCTION. Thoracentesis with imaging guidance is a bedside or outpatient clinic procedure that permits pleural fluid to be rapidly sampled, visualized, and analyzed for chemical, microbiologic, and cellular content. 2 de nov. de 2023 · Compre ingressos para Circo Castelli |CATALÃO /ESTREIA em Catalão dia 02/11. Confira os melhores eventos da Sympla! Não Circo Castelli Horários De segunda a sexta 20:30 Sábado, Domingo e feriados 16:00 18:00h e 20:30 +info: seção "contato" @circocastelli @fernandalincoln Mapa do circo @circocastellioficial Fale com o .
{plog:ftitle_list}
web24 de mai. de 2021 · Armação dos Búzios. Avenida José Bento Ribeiro Dantas, número 10274 – Armação dos Búzios / Telefone: (22) 99886-6720 / Horário de Atendimento: Das 07h às 23h. Covid-19: Drogaria São Paulo .
INTRODUCTION. Thoracentesis with imaging guidance is a bedside or outpatient clinic procedure that permits pleural fluid to be rapidly sampled, visualized, and analyzed for chemical, microbiologic, and cellular content.Pleural fluid analysis in adults with a pleural effusion. Author John E Heffner, MD . Pleural fluid testing involves removing a sample of this fluid so that it can be analyzed using one or more laboratory methods. Testing is used to diagnose the cause of an . A pleural fluid analysis is a group of tests that examine a sample of abnormal fluid that builds up in the space between your lungs and chest wall. This space is called the pleural space. The pleura is a thin tissue that covers .
Pleural effusion is excess fluid accumulation in the pleural space caused by disease or physiologic dysregulation and requires careful investigation to identify the underlying cause. A. pleural fluid analysis (PFA) Coagulation considerations re: thoracentesis or pigtail drain insertion.
Pleural effusion occurs when fluid collects between the parietal and visceral pleura. Processes causing a distortion in body fluid mechanics, such as in heart failure or nephrotic syndrome,. Pleural fluid analysis is the analysis of pleural fluid in the laboratory that occurs after a pleural tap, or thoracentesis. A thoracentesis is a procedure used to drain excess fluid from the.
Pleural fluid analysis is a test that examines a sample of fluid that has collected in the pleural space. This is the space between the lining of the outside of the lungs (pleura) and .Laboratory testing helps to distinguish pleural fluid transudates from exudates. However, certain types of exudative pleural effusions might be suspected simply by observing the gross. Pleural fluid analysis is the analysis of pleural fluid in the laboratory that occurs after a pleural tap, or thoracentesis.
Selecting appropriate laboratory tests based on available evidence is central to improve clinical effectiveness and impacting on patient outcome. Although long studied, there is no mutual agreement upon pleural fluid (PF) management in the laboratory context. Given the experienced confusion about th . Pleural fluid is found in the pleural cavity and serves as a lubricant for the movement of the lungs during inhalation and exhalation. It is derived from a plasma filtrate from blood capillaries and is found in small quantities between the layers of the pleurae – membranes that cover the chest cavity and the outside of each lung.. A variety of conditions and diseases . If pleural fluid analysis and chest CT (for pulmonary emboli and abnormality in the chest) are not helpful for identifying the cause of pleural effusions, other options should be followed. 1. Observation. Observation is the best action if the patient is improving, such as pleural effusion due to viral illness that is self-limited. If pleural .
Laboratory testing helps to distinguish pleural fluid transudates from exudates. However, certain types of exudative pleural effusions might be suspected simply by observing the gross characteristics of the fluid obtained during thoracentesis. . The value of pleural fluid analysis. Am J Med Sci. 2008 Jan. 335(1):7-15. [QxMD MEDLINE Link . Laboratory analysis of the pleural fluid is crucial for differentiating between transudative and exudative effusions. A sample of the fluid is obtained through a procedure called thoracentesis. The fluid is then sent to a laboratory for analysis. Various tests, including cell count, protein levels, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) levels, pH, and .
Clin Chem Lab Med. 2022 Nov 17;61(5):921-934. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2022-0844. Print 2023 Apr 25. . observer independence and short turn-around time. Here, we reviewed the past, present and future of pleural fluid biochemical analysis. We reviewed the history of Light's criteria and its modifications and the current status of biomarkers for heart .
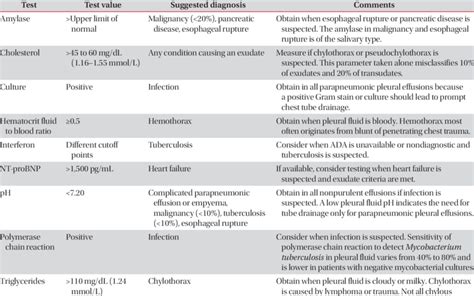
CEA is raised in case of pleural effusion due to GIT malignancy. This may be raised in the case of breast carcinoma. Exudate: Pleural fluid cholesterol >60 mg/dL. Pleural fluid cholesterol: serum cholesterol = >0.3; Pleural fluid bilirubin: serum bilirubin = 0.6 or more. Transudate: Proteins are <3 g/dL. What is the microscopic examination of .Previous use of antibacterial agents affected the bacteriologic analysis of pleural fluid in this pediatric sample admitted for PPE. However, it did not interfere significantly with biochemical parameters of pleural fluid. . Impact of antibiotic therapy on laboratory analysis of parapneumonic pleural fluid in children J Pediatr Surg. 2011 Mar . In addition to its diagnostic value, pleural fluid analysis also has predictive value (ie, estimates of the likelihood of a clinical response to pleural fluid drainage) and prognostic value (eg, likelihood of disease recurrence or progression in malignant pleural effusion). The initial approach to pleural fluid analysis will be presented here.
pleural fluid test list
1. Pleural fluid The pulmonary pleurae are two thin serous membranes that surround the lungs and line the inside of the thoracic cavity with a layer of mesothelium. The pleural cavity lies between these layers of mesothelium and contains physiologically a clear serous fluid of less than 15 mL. A pleural effusion results from excessive
Abbreviations AIC, Akaike information criterion; MPE. malignant pleural effusion. Introduction. A malignant pleural effusion (MPE) signifies advanced malignancy and a poor prognosis, with a median survival of 3–12 months. 1 Rapid diagnosis is important to inform prognosis and management. International guidelines recommend thoracentesis to obtain pleural fluid for . Body fluid or cavity fluid is the fluid that covers our vital organs that not only reduces friction between the membranes but also delivers oxygen and nutrients to the cells, and takes away waste materials, which are then eliminated with urination. e.g. pleural fluid around the lung, pericardial fluid around the heart, and peritoneal fluid around the abdominal and . Pleural fluid serves a physiologic function in respiration, while also being a useful measure to diagnose and assess disease, trauma, and other abnormalities. A brief review of the anatomy and physiology of normal pleural fluid gives a point of reference for assessing the causes of abnormal pleural fluid collections and pleural effusions. [1][2][3]
The proper analysis of pleural fluid requires the coordinated efforts of several clinical laboratory departments including clinical chemistry, hematology, microbiology, and cytopathology. However, the first step in fluid analysis is one of .
The preanalytical errors in pleural fluid biochemistry remain largely unknown. Taken together, this series focuses on the analytical and clinical aspects of pleural fluid analysis, with the overall aim of providing novel insights into the field of pleural fluid analysis for both clinicians and laboratory specialists. pleural fluid analysis & clinical definition of a complicated parapneumonic effusion. Several criteria are used to predict the need for chest tube drainage (which clinically defines a complex parapneumonic effusion). .Pleural effusion occurs when fluid collects between the parietal and visceral pleura. Processes causing a distortion in body fluid mechanics, such as in heart failure or nephroticIf more than a 24-hour delay is anticipated between collection and receipt in the laboratory, please add the following: 1 mL (1000 units) of heparin for each 300 mL of collected fluid. To the entire volume (up to 1 liter) add an equal volume of 50% ethyl alcohol or Saccomanno fixative.
Laboratory Medicine Summary. Diagnostic analysis of pleural fluid. Pleural fluid is labeled and sent for diagnostic analysis. If the effusion is small and contains a large amount of blood, the fluid should be placed in a blood tube with anticoagulant so that it does not clot. The following laboratory tests should be requested:The analysis will then provide a differential diagnosis which will affect treatment modalities. . Laboratory Findings. Once a pleural effusion is diagnosed, the cause must be determined. Pleural fluid is drawn out of the pleural space in a process called thoracentesis. A needle is inserted through the back of the chest wall into the pleural .
Pleural effusion is a collection of fluid around your lungs. Your provider has to get rid of this fluid and treat the condition that caused it to build up. . Thoracentesis or biopsy (inserting a needle between your ribs to remove a fluid sample). Pleural fluid analysis (examining the fluid from the pleural space). If less invasive tests don .
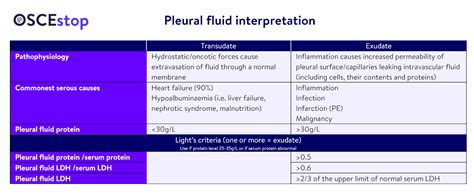
Pleural effusions are usually categorized as. Transudates. Exudates. Categorization of the effusions is based on laboratory characteristics of the fluid (see table Criteria for Identifying Exudative Pleural Effusions).Whether unilateral or bilateral, a transudate can usually be treated without extensive evaluation, whereas the cause of an exudate requires investigation.The specific gravity of pleural fluid can vary, but it is typically around 1.012 to 1.022. This range reflects the relative concentration of solutes and particles in the pleural fluid compared to water. Specific gravity is an important parameter used in the analysis of pleural fluid to assess whether the fluid is transudative or exudative.
pleural fluid studies interpretation
Test ordering in pleural fluid analysis. The preanalytical phase of pleural fluid laboratory testing starts with test requesting: the right test should be ordered in the right time for the right patient ().Pleural fluid samples sent to the laboratory should be accompanied with a test request form or its electronic equivalent.
Selecting appropriate laboratory tests based on available evidence is central to improve clinical effectiveness and impacting on patient outcome. Although long studied, there is no mutual agreement upon pleural fluid (PF) management in the laboratory context. Pleural complications in lung transplantation; Pleural fluid analysis in adults with a pleural effusion; Protein-losing gastroenteropathy; Pulmonary tuberculosis disease in adults: Clinical manifestations and complications; Sequelae and complications of pneumonectomy; Sporadic lymphangioleiomyomatosis: Clinical presentation and diagnostic .
WEBJUPITERWEB - O PORTAL DA GRADUAÇÃO. O Jupiter é o portal da graduação da Universidade de São Paulo, para acessa-lo é necessário inserir o login e utilizar seus recursos. Acesse Jupiter. O login expira anualmente, sendo necessário alterar a senha. Esse procedimento e o aviso de vencimento da senha é notificado por email.
laboratory analysis of pleural fluid|pleural fluid lab tests